| Home | All Classes | Main Classes | Annotated | Grouped Classes | Functions |
The QCursor class provides a mouse cursor with an arbitrary shape. More...
#include <qcursor.h>
Inherits Qt.
The QCursor class provides a mouse cursor with an arbitrary shape.
This class is mainly used to create mouse cursors that are associated with particular widgets and to get and set the position of the mouse cursor.
Qt has a number of standard cursor shapes, but you can also make custom cursor shapes based on a QBitmap, a mask and a hotspot.
To associate a cursor with a widget, use QWidget::setCursor(). To associate a cursor with all widgets (normally for a short period of time), use QApplication::setOverrideCursor().
To set a cursor shape use QCursor::setShape() or use the QCursor constructor which takes the shape as argument, or you can use one of the predefined cursors defined in the CursorShape enum.
If you want to create a cursor with your own bitmap, either use the QCursor constructor which takes a bitmap and a mask or the constructor which takes a pixmap as arguments.
To set or get the position of the mouse cursor use the static methods QCursor::pos() and QCursor::setPos().
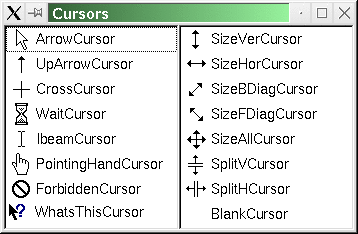
See also QWidget, GUI Design Handbook: Cursors, Widget Appearance and Style, and Implicitly and Explicitly Shared Classes.
On X11, Qt supports the Xcursor library, which allows for full color icon themes. The table below shows the cursor name used for each Qt::CursorShape value. If a cursor cannot be found using the name shown below, a standard X11 cursor will be used instead. Note: X11 does not provide appropriate cursors for all possible Qt::CursorShape values. It is possible that some cursors will be taken from the Xcursor theme, while others will use an internal bitmap cursor.
| Qt::CursorShape Values | Cursor Names |
|---|---|
| Qt::ArrowCursor | left_ptr |
| Qt::UpArrowCursor | up_arrow |
| Qt::CrossCursor | cross |
| Qt::WaitCursor | wait |
| Qt::IbeamCursor | ibeam |
| Qt::SizeVerCursor | size_ver |
| Qt::SizeHorCursor | size_hor |
| Qt::SizeBDiagCursor | size_bdiag |
| Qt::SizeFDiagCursor | size_fdiag |
| Qt::SizeAllCursor | size_all |
| Qt::SplitVCursor | split_v |
| Qt::SplitHCursor | split_h |
| Qt::PointingHandCursor | pointing_hand |
| Qt::ForbiddenCursor | forbidden |
| Qt::WhatsThisCursor | whats_this |
See CursorShape for a list of shapes.
See also setShape().
bitmap and mask make up the bitmap. hotX and hotY define the cursor's hot spot.
If hotX is negative, it is set to the bitmap().width()/2. If hotY is negative, it is set to the bitmap().height()/2.
The cursor bitmap (B) and mask (M) bits are combined like this:
Use the global color color0 to draw 0-pixels and color1 to draw 1-pixels in the bitmaps.
Valid cursor sizes depend on the display hardware (or the underlying window system). We recommend using 32x32 cursors, because this size is supported on all platforms. Some platforms also support 16x16, 48x48 and 64x64 cursors.
See also QBitmap::QBitmap() and QBitmap::setMask().
pixmap is the image. It is usual to give it a mask (set using QPixmap::setMask()). hotX and hotY define the cursor's hot spot.
If hotX is negative, it is set to the pixmap().width()/2. If hotY is negative, it is set to the pixmap().height()/2.
Valid cursor sizes depend on the display hardware (or the underlying window system). We recommend using 32x32 cursors, because this size is supported on all platforms. Some platforms also support 16x16, 48x48 and 64x64 cursors.
Currently, only black-and-white pixmaps can be used.
See also QPixmap::QPixmap() and QPixmap::setMask().
Creates a cursor with the specified window system handle handle.
Warning: Portable in principle, but if you use it you are probably about to do something non-portable. Be careful.
See also initialize().
Warning: Portable in principle, but if you use it you are probably about to do something non-portable. Be careful.
See also cleanup().
You can call QWidget::mapFromGlobal() to translate it to widget coordinates.
See also setPos(), QWidget::mapFromGlobal(), and QWidget::mapToGlobal().
Examples: chart/canvasview.cpp, fileiconview/qfileiconview.cpp, and menu/menu.cpp.
You can call QWidget::mapToGlobal() to translate widget coordinates to global screen coordinates.
See also pos(), QWidget::mapFromGlobal(), and QWidget::mapToGlobal().
See CursorShape for the list of cursor shapes.
See also shape().
See also setShape().
See also Format of the QDataStream operators.
See also Format of the QDataStream operators.
This file is part of the Qt toolkit. Copyright © 1995-2003 Trolltech. All Rights Reserved.
| Copyright © 2003 Trolltech | Trademarks | Qt version 3.2.0b2
|